7,810 تومان
در حال حاضر موجود نمی باشد
موجودی در حال ارسال به انبار
-
2000 عدد1404/09/22
علاقه مندان : 11 نفر
وضعیت : فعال
تعداد مرجوعی : 0
دنبال کنندگان : 18 نفر
قدمت : 10 سال و 2 ماه و 23 روز
وزن : 2 گرم
کل فروش : 29494 عدد
تعداد سفارش ها : 1144 سفارش
4 از 5.0 با 10 رای
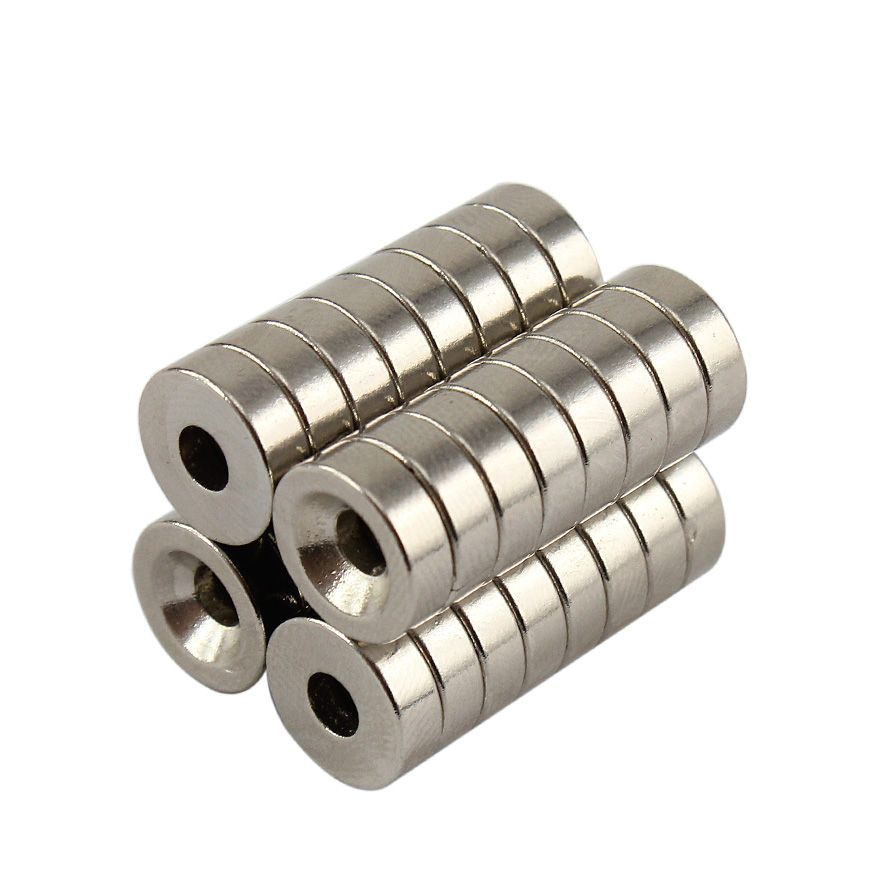
آهن ربای نئودمیوم بسیار قوی 12mm X 3.5mm گرد
توجه: ضخامت اهن ربا کم و زیاد دارد احتمال یکسان بودن همه آهن ربا وجود ندارد در این پارت
نئودیمیم عنصر شیمیایی است که در جدول تناوبی با نشان Nd و عدد اتمی ۶۰ معرفی شدهاست. آهن ربای نئودیمیوم آهن بور (NdFeB) از گروه آهن رباهای خاکی کمیاب بوده و عناصر اصلی تشکیل دهنده آن عبارت از Fe، Nd و B می باشند. در زیر دمای °C 150 آهن ربای NdFeB قوی ترین آهن ربای موجود شناخته در دنیا محسوب می شود. به دلیل قدرت بسیار بالای این آهن ربا، برای اکثر کاربردهای دما پایین، NdFeB اولین انتخاب می باشد. انواع مختلفی از آهن ربای NdFeB وجود دارد که بر اساس قدرت و دمای کاری، با یکدیگر متفاوت هستند. در حال حاضر آهن ربای N50، قوی ترین آهن ربای تجاری موجود در دنیا است.
از آهنربا نیودمیوم می توان در پرینترهای سه بعدی استفاده کرد. این محصول به شکل دایره به قطر 12 میلی متر و با ضخامت 3.5 میلی متر می باشد.
کاربرد آهن ربای نئودمیوم :
- ژنراتورها (برای مثال در توربین های بادی، توربوژنراتورها و غیره)
- موتورها (برای مثال در ماشین های ظرفشویی، دریل، مخلوط کن ها، جاروبرقی، خشک کن و غیره)
- سنسورها
- سیستم های تعلیق مغناطیسی
- میکروفون و هدفون
- جداکننده های مغناطیسی
- آهن رباهای به کار رفته در هارددرایو کامپیوتر
- یاتاقان های مغناطیسی
- سیستم های ایجااد حالت شناوری مغناطیسی
- گیره های آهن ربایی
- سیستم های ABS
- پرینتر سه بعدی
مشخصات آهن ربای نئودمیوم :
- ابعاد: قطر 12 میلی متر و ضخامت 3.5 میلی متر
- شار در مرکز آهنربا : حدود 4000 گاوس
- گرید: N30
Description:
A neodymium magnet (also known as NdFeB, NIB or Neo magnet) is the most widely used type of rare-earth magnet. It is a permanent magnet made from an alloy of neodymium, iron, and boron to form the Nd2Fe14B tetragonal crystalline structure. Developed independently in 1984 by General Motors and Sumitomo Special Metals, neodymium magnets are the strongest type of permanent magnet available commercially. Because of different manufacturing processes, they are divided into two subcategories, namely sintered NdFeB magnets and bonded NdFeB magnets. They have replaced other types of magnets in many applications in modern products that require strong permanent magnets, such as electric motors in cordless tools, hard disk drives, and magnetic fasteners.
Neodymium magnets are graded according to their maximum energy product, which relates to the magnetic flux output per unit volume. Higher values indicate stronger magnets. For sintered NdFeB magnets, there is a widely recognized international classification. Their values range from 28 to 52. The first letter N before the values is short for neodymium, meaning sintered NdFeB magnets. Letters following the values indicate intrinsic coercivity and maximum operating temperatures (positively correlated with the Curie temperature), which range from the default (up to 80 °C or 176 °F) to AH (230 °C or 446 °F)
Neodymium magnets are used in numerous applications requiring strong, compact permanent magnets, such as electric motors for cordless tools, hard disk drives, magnetic hold downs, and jewelry clasps.
Application:
3D printers
Generators
Motors
Sensors
Microphone and headphones
Magnetic separators
Magnets used in computer hard drives
Magnetic bearings
Magnetic clips
ABS systems
Features:
Size: diameter12 mm thickness of 3.5 mm hole 4mm
Grade: N30
Gauss: 4000GS
Magnetization Directions: NS pole ends of the plane
Temperature: 80 degrees or less