5 از 5.0 با 4 رای
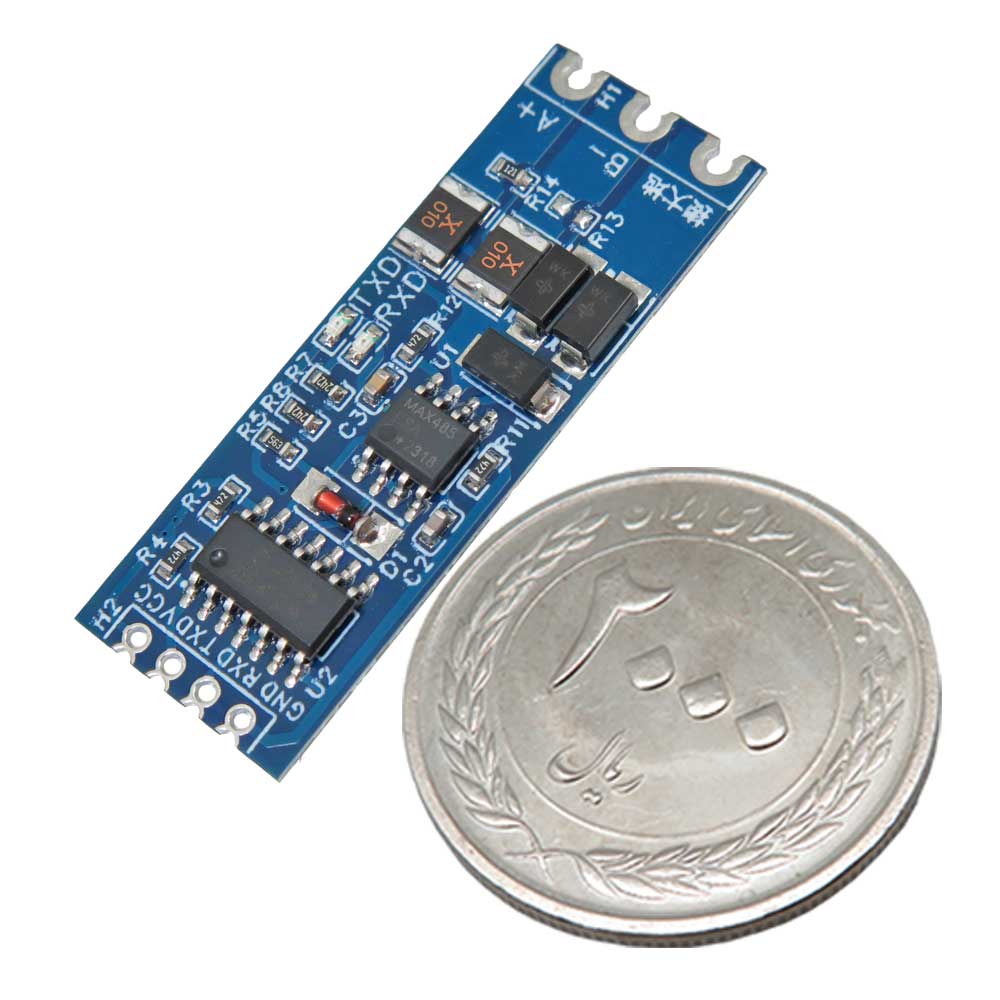
ماژول تبدیل TTL به RS485
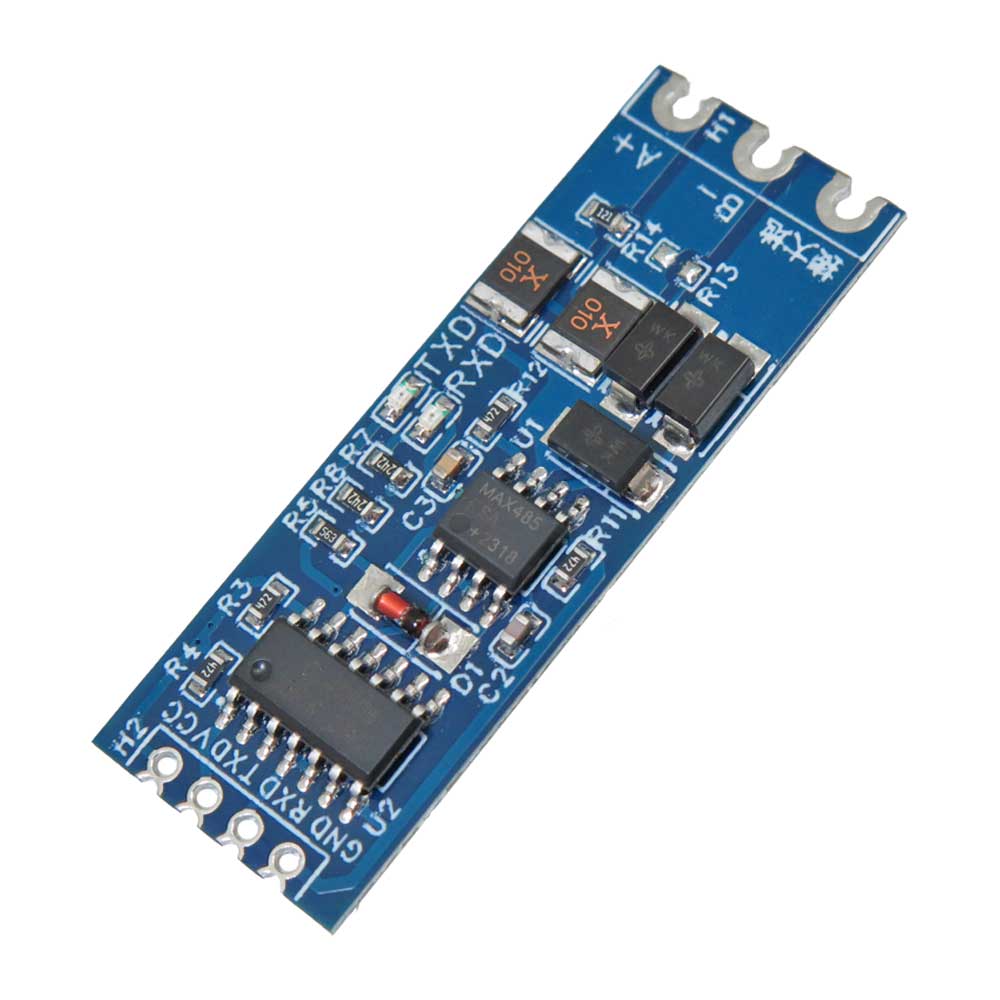
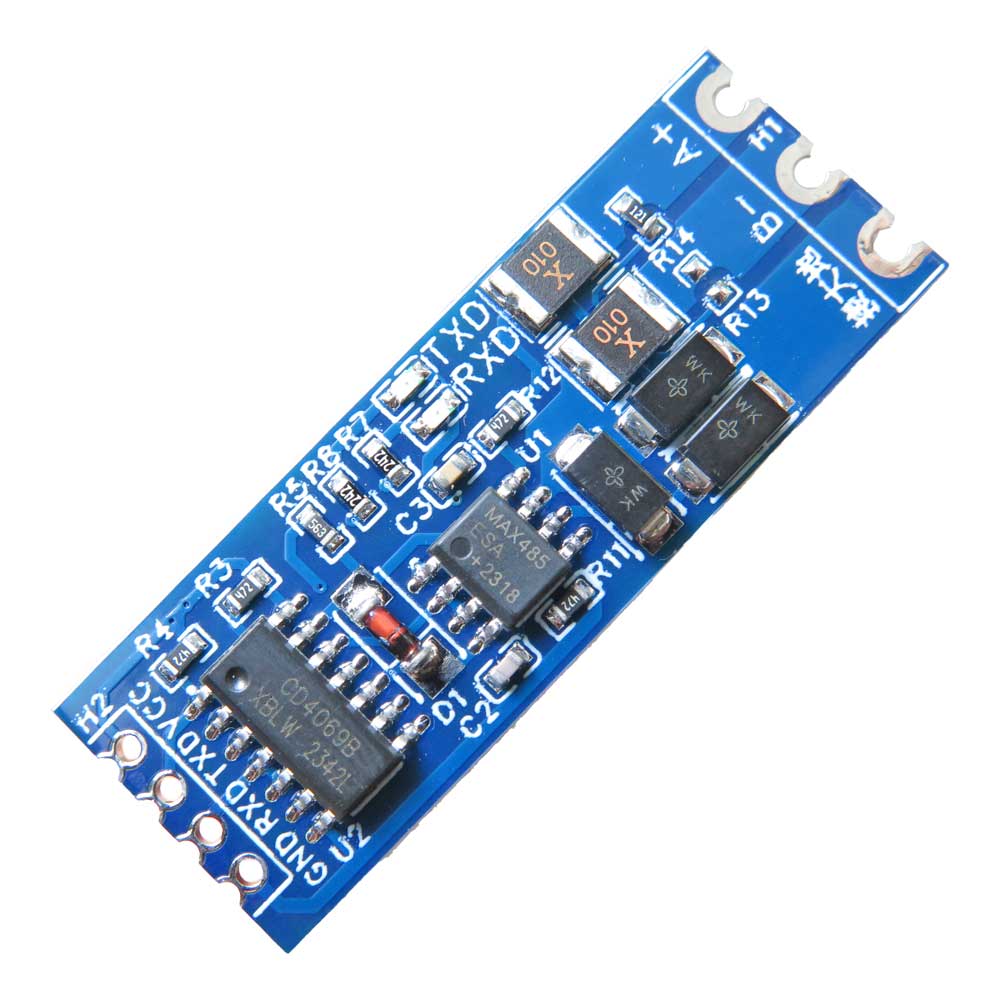
این ماژول با ولتاژ تغذیه 3.3 ولت و 5.0 ولت سازگار است و از سیگنال هایی در همین بازه ولتاژی پشتیبانی میکند . استفاده از تراشه های صنعتی وارداتی ، امکان کار در بازه دمایی 40- تا 85+ درجه سانتی گراد را فراهم کرده است . همچنین طراحی استاندارد با گام پایه 2.54 میلی متر و ضخامت 0.8 میلی متر ، باعث شده نصب آن روی بردهای چاپی یا استفاده به صورت لحیم کاری مستقیم آسان باشد . مقاومت تطبیقی 120 اهم نیز در مدار وجود دارد تا از کیفیت انتقال در فواصل طولانی محافظت شود .
مبدل سریال TTL به RS485 دو طرفه برای پروژه هایی که نیاز به تبادل داده در فواصل بالا و محیط های صنعتی دارند گزینه ای مطمئن و کاربردی است . این ماژول به صورت خودکار جهت ارسال و دریافت داده را تشخیص میدهد و دیگر نیازی به استفاده از پایه های DE یا RE نمیباشد . دارای 4 پایه برای اتصال مستقیم به میکروکنترلر است و از قابلیت hot swap نیز پشتیبانی میکند . نشانگرهای ال ای دی (LED) برای سیگنال های RXD و TXD به شما این امکان را میدهند که وضعیت ارسال و دریافت داده را در لحظه بررسی کنید .
کاربرد :
- ارتباط بین چند میکروکنترلر در سیستم های اتوماسیون صنعتی
- انتقال داده در شبکه های کنترل از راه دور تا فاصله 1000 متر
- استفاده در پروژه های خانه هوشمند برای اتصال سنسورها و تجهیزات مختلف
- راه اندازی سیستم های حفاظتی و امنیتی با پروتکل RS485
مشخصات فنی ماژول مبدل TTL به RS485 :
- نوع مبدل : سریال TTL به RS485 دو طرفه
- ولتاژ تغذیه : 3.3 ولت و 5.0 ولت
- سیگنال ورودی : سازگار با 3.3 ولت و 5.0 ولت
- فاصله انتقال داده : تا 1000 متر
- سرعت انتقال : تا 2.5 مگابیت بر ثانیه
- تعداد دستگاه پشتیبانی شده : تا 32 دستگاه روی یک باس
- مقاومت تطبیقی : 120 اهم
- طراحی پایه : گام 2.54 میلی متر
- ضخامت برد : 0.8 میلی متر (نیمه سوراخ)
- محدوده دمای کاری : منفی 40 درجه سانتی گراد تا مثبت 85 درجه سانتی گراد
- محافظت : ضد صاعقه و ضد تداخل الکترومغناطیسی
- قابلیت تعویض داغ : پشتیبانی از Hot Swap
- کنترل جهت انتقال : خودکار بدون نیاز به پایه های DE و RE
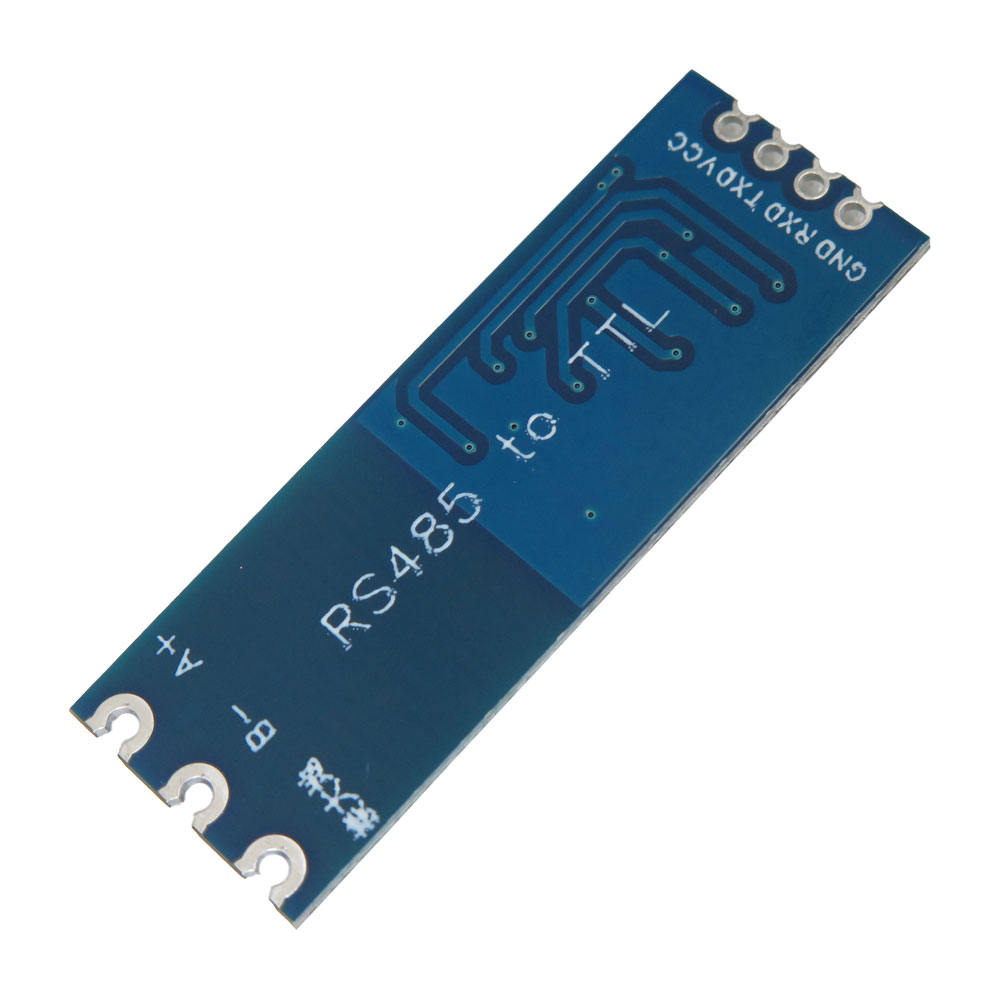
- اتصال به میکروکنترلر : هدر 4 پین
- نشانگر وضعیت : ال ای دی های TXD و RXD
- نوع سیگنال انتقال : سیگنال تفاضلی برای کاهش نویز
- محافظت اضافی : دارای فیوز پلی و دیود محافظ ولتاژ گذرا
امکانات :
- کنترل خودکار جهت انتقال داده بدون نیاز به پایه های اضافه
- پشتیبانی از اتصال همزمان تا 32 دستگاه روی یک باس
- طراحی مقاوم در برابر نویز و محافظت در برابر نوسانات ولتاژ و صاعقه
- امکان تعویض داغ برای جلوگیری از قطعی و تداخل در ارتباطات
Description:
The SCM TTL to RS-485 Interface module provides a robust automatic bi-directional interface from TTL to long-line RS-485. This converter is generally used for industrial automation. This module includes lightning protection design and anti-jamming design. The GND terminal is at the end of the module, so that lightning protection and anti-interference can be achieved. It uses a standard 2.54 mm pitch design.It also includes 120-ohm matching resistance. It supports communication between multiple microcontrollers, allowing up to 32 devices on the bus. It can be hot-swappable, in order to prevent signal interference. The module has a 4-pin header on the assembly for connections to the MCU. It automatically takes care of data transmission direction control, so it does not require the extra DE/RE pins required by most other RS-485 modules.
Highlights:
1. Compatible with 3.3V and 5.0V power supply.
2. Compatible with 3.3V and 5.0V signal.
3. Absolute using imported chips; industrial design; anti-interference ability; while using more effective 485 lightning protection design can be used in the industrial field and harsh field environments; the working temperature of -40 ℃ to + 85 ℃; transmission distance up to 1 kilometer (made with 850 meters of cable F1.5 tests recommended using in the 800 meters, when more than 800m please add repeaters).
4. Semi-hole process design, thickness 0.8mm, can easily use as a picture board, it can also be welded terminal use.
5. Has RXD, TXD signal indicator lights, monitor send and receive status.
Features:
Transmit and receive indicator LEDsSpeeds up to 2.5Mbit/Sec
Uses differential signaling for noise immunity
Multi-drop supports up to 32 devices on the same bus
Built-in poly fuses for over-current protection
Built-in transient surge protection diodes for over-voltage protection
Arduino code example:
Master RS-485 Device Software
/* * SCM TTL To RS485 Master Software * Exercise the SCM TTL to RS485 Module. This code runs on the first (Master)device. * Use the SCM_RS485_Slave_Test software for the second (Slave) device * This uses the SoftSerial.h library which comes with the Arduino IDE * Pins used for the soft serial port are fairly arbitrary and can be changed * as needed. Just redefine them below. */ #include <SoftwareSerial.h> const int SSERIAL_RX_PIN = 10; //Soft Serial Receive pin const int SSERIAL_TX_PIN = 11; //Soft Serial Transmit pin // Create Soft Serial Port object and define pins to use SoftwareSerial RS485Serial(SSERIAL_RX_PIN, SSERIAL_TX_PIN); // RX, TX int byteReceived; //=============================================================================== // Initialization //=============================================================================== void setup() { Serial.begin(9600); // Start the built-in serial port Serial.println("Master Device"); Serial.println("Type in upper window, press ENTER"); RS485Serial.begin(9600); // Start the RS485 soft serial port } //=============================================================================== // Main //=============================================================================== void loop() { if (Serial.available()) // A char(byte) has been entered in the Serial Monitor { byteReceived = Serial.read(); // Read the byte RS485Serial.write(byteReceived); // Send byte to Remote Arduino } if (RS485Serial.available()) //Data from the Slave is available { byteReceived = RS485Serial.read(); // Read received byte Serial.write(byteReceived); // Show on Serial Monitor } }
Slave RS-485 Device Software
/* * SCM TTL to RS485 Slave Software * Exercise the SCM TTL to RS485 Module. This code runs on the second (slave)device. * Use the SCM_RS485_Master_Test software for the first (Master) device * This uses the SoftSerial.h library which comes with the Arduino IDE * Pins used for the soft serial port are fairly arbitrary and can be changed * as needed. Just redefine them below. */ #include <SoftwareSerial.h> const int SSERIAL_RX_PIN = 10; //Soft Serial Receive pin const int SSERIAL_TX_PIN = 11; //Soft Serial Transmit pin // Create Soft Serial Port object and define pins to use SoftwareSerial RS485Serial(SSERIAL_RX_PIN, SSERIAL_TX_PIN); int byteReceived; int byteSent; //=============================================================================== // Initialization //=============================================================================== void setup() { Serial.begin(9600); // Start the built-in hardware serial port Serial.println("Slave Device"); RS485Serial.begin(9600); // Start the RS485 soft serial port } //=============================================================================== // Main //=============================================================================== void loop() { // Watch for data coming in on the soft serial port. If found, send a copy to the // hardware port to display on the local serial terminal and also echo a copy back out // the soft serial port to the Master device if (RS485Serial.available()) // If data has come in from Master { byteSent = RS485Serial.read(); // Read the byte Serial.write(byteSent); // Show on local Serial Monitor window delay(10); RS485Serial.write(byteSent); // Send the byte back to Master } }